Kotlin
A concise multiplatform language developed by JetBrains
Update your Kotlin projects for Android Gradle Plugin 9.0
Android Gradle plugin 9.0 is now available, and it includes two major changes that will affect existing Kotlin projects:
- Android apps need to start using AGP 9.0’s built-in Kotlin support.
- Kotlin Multiplatform projects targeting Android need to migrate to the new Android KMP library plugin.
This post provides some details about these changes and points you to the resources that you’ll need to update your existing projects.
You’ll also need to update tools and plugins that depend on AGP to their latest versions with support for AGP 9.0. If you use Android Studio, you’ll need to use Otter 3 Feature Drop or later.
Note: Support for AGP 9.0 is coming soon to IntelliJ IDEA, expected to arrive in Q1 2026.
For information about Gradle plugin compatibility, you can refer to this community-maintained page.
We are working on adopting AGP 9.0 in our documentation, samples, and wizards. This means that they will all use AGP 9.0 by default and already include these changes in their respective configurations.
Use built-in Kotlin
Previously, Android projects had to apply the Kotlin Android plugin (org.jetbrains.kotlin.android) to add support for Kotlin source files. With AGP 9.0, Kotlin support is built in and enabled by default, so you no longer need to apply the Kotlin Android plugin separately for Android apps.
The main migration step here is to remove usages of the Kotlin Android plugin from your projects. However, if your project uses kapt for annotation processing or sets custom kotlinOptions, you’ll need to update those configurations as well.
Read the migration guide in the Android documentation for step-by-step instructions.
With AGP 9.0, you can still opt out of these changes temporarily by adding
android.builtInKotlin=falseandandroid.newDsl=falseto yourgradle.properties. However, this will no longer work in AGP 10.0, which is expected sometime in 2026.
Use the new Android KMP library plugin
In previous versions, the Android Gradle plugin provided two different plugins you could apply to a module:
- The Android library plugin (
com.android.library). - The Android application plugin (
com.android.application).
Either of them could be used in combination with the KMP plugin (org.jetbrains.kotlin.multiplatform) to set up a multiplatform module.
AGP 9.0 introduces a new, simplified Android KMP library plugin (com.android.kotlin.multiplatform.library), built specifically for multiplatform projects. The previously used Android library and Android application plugins are no longer compatible with the KMP plugin in the same module, which means you’ll need to migrate any multiplatform modules to the new plugin. This migration will be different for library and application modules; you can learn more about both scenarios below.
With AGP 9.0, you can still opt out of these changes temporarily by adding
android.enableLegacyVariantApi=trueto yourgradle.properties. However, this will no longer work in AGP 10.0, which is expected sometime in 2026.
Migrating a library module
If you have a module that uses the Android library plugin and the Kotlin Multiplatform plugin together, you’ll have to replace the Android library plugin with the Android KMP library plugin. This means you’ll have to update the build configuration of your existing module, but generally no changes are required to your project structure or source code.
The new Android KMP library plugin has default settings that are designed for Kotlin Multiplatform and optimized for build speed and stability. Some previous configuration options have been removed or moved to new APIs.
Read the migration guide to learn about the differences and get step-by-step instructions on how to migrate a library module to the new plugin.
Migrating an application module
Many projects apply both the Android application plugin and the Kotlin Multiplatform plugin in the same module. A module like this contains shared multiplatform code as well as an Android application with all of its related build configuration. This was the recommended structure in the past, and if you created your project using the KMP wizard, your project probably has a single composeApp module that’s set up like this.
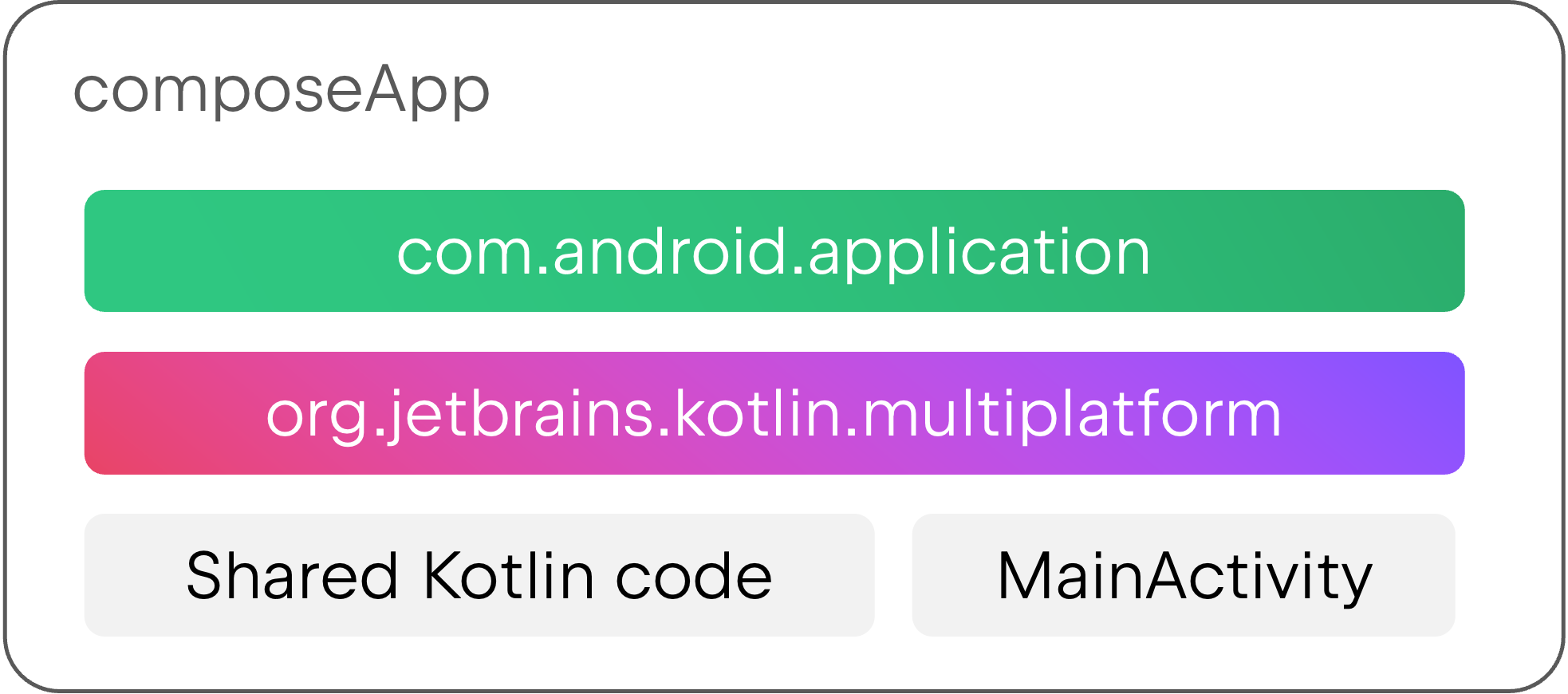
Modules like this also have to be migrated to use the new Android KMP library plugin in the module that contains shared code, which requires multiple steps.
First, you’ll have to create a new module for the entry point of your app and apply the Android application plugin there. This new module can be relatively small and simple, containing the build configuration to package an Android app and its entry point, such as Activity and Application classes (all represented by MainActivity in the illustrations here).
When using AGP 9.0, this new module doesn’t need to apply a Kotlin plugin, as it can use the built-in Kotlin support (as detailed above).
Then, this new application module should depend on the existing multiplatform module to have access to its contents. The multiplatform module can now become an Android library, which means you should migrate it to the new Android KMP library plugin.
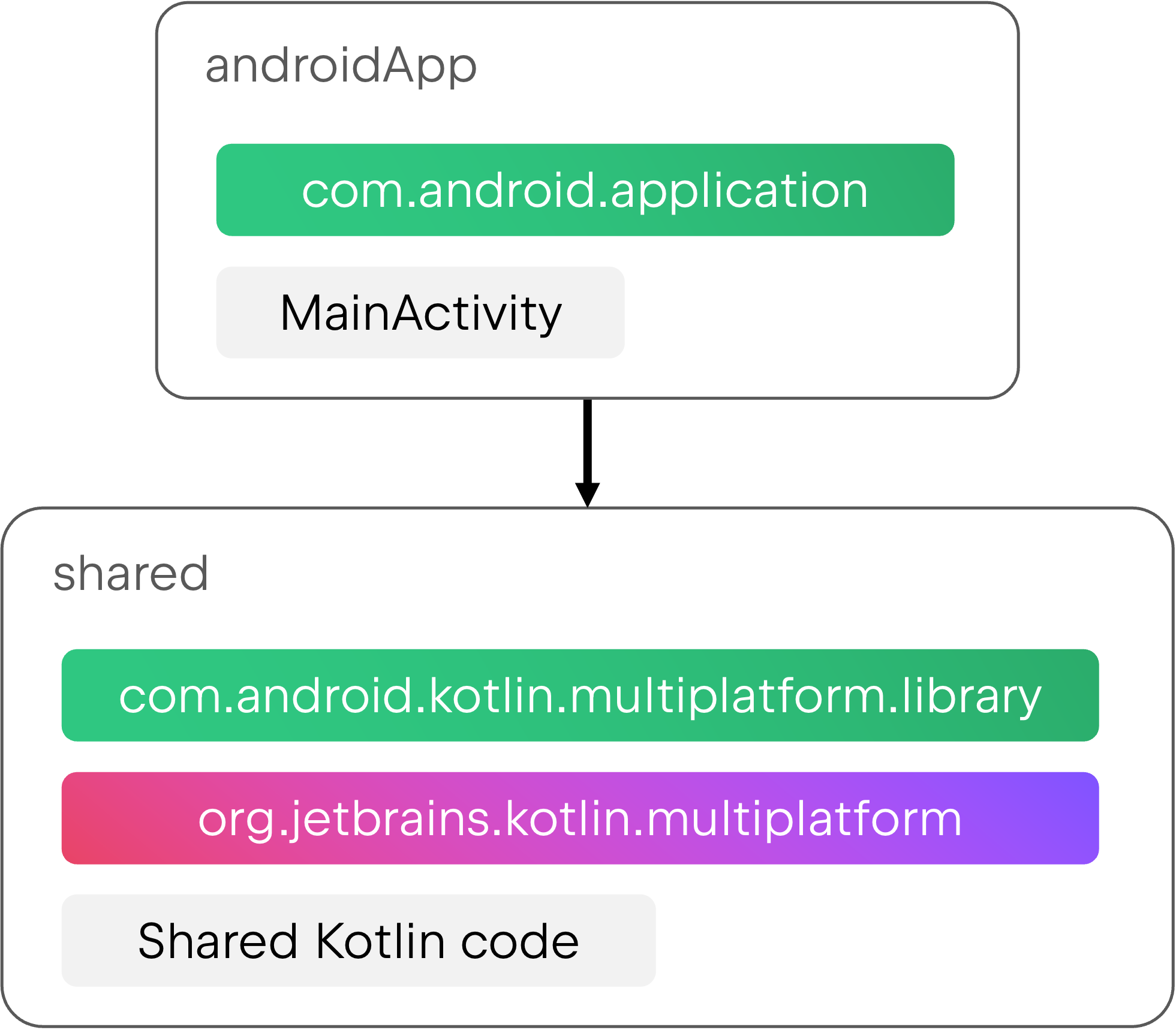
To migrate an Android application module to AGP 9.0, follow the detailed steps in the migration guide.
Conclusion
We recommend making these configuration changes in your existing projects as soon as possible to ensure smooth upgrades to the latest versions of AGP in the future.
In addition to the links above, you can read the full release notes for AGP 9.0 to learn more about what’s new.
If you encounter any issues with AGP 9.0 itself, create a new issue in the Android Studio component of the Google issue tracker.
For problems related to the Kotlin Multiplatform IDE plugin, create an issue in the KMT tracker.
To provide feedback on Kotlin documentation, create an issue on YouTrack or report it in the #multiplatform channel on the Kotlinlang Slack.
Subscribe to Kotlin Blog updates







