IntelliJ IDEA
IntelliJ IDEA – the IDE for Professional Development in Java and Kotlin
Spring Boot Endpoints and Kotlin
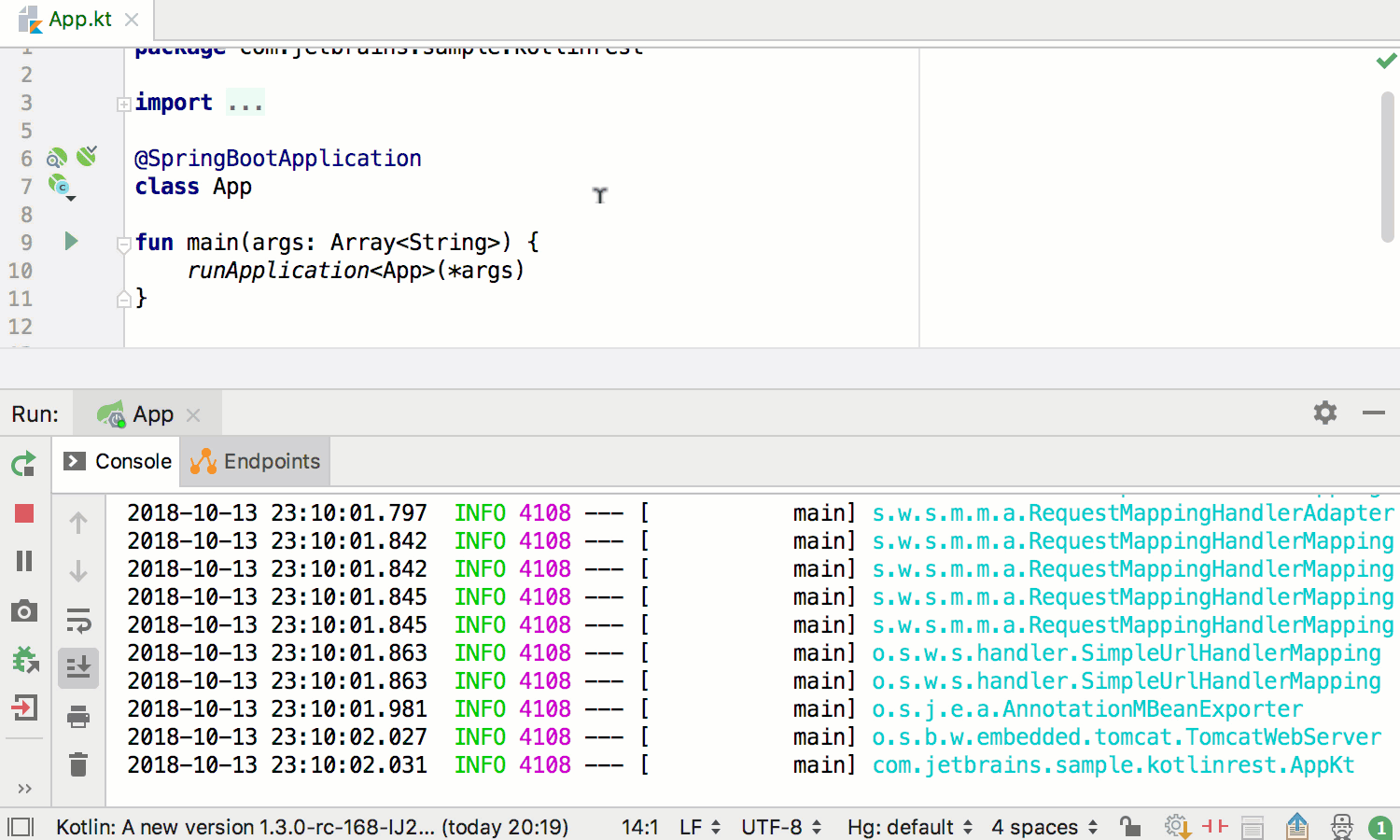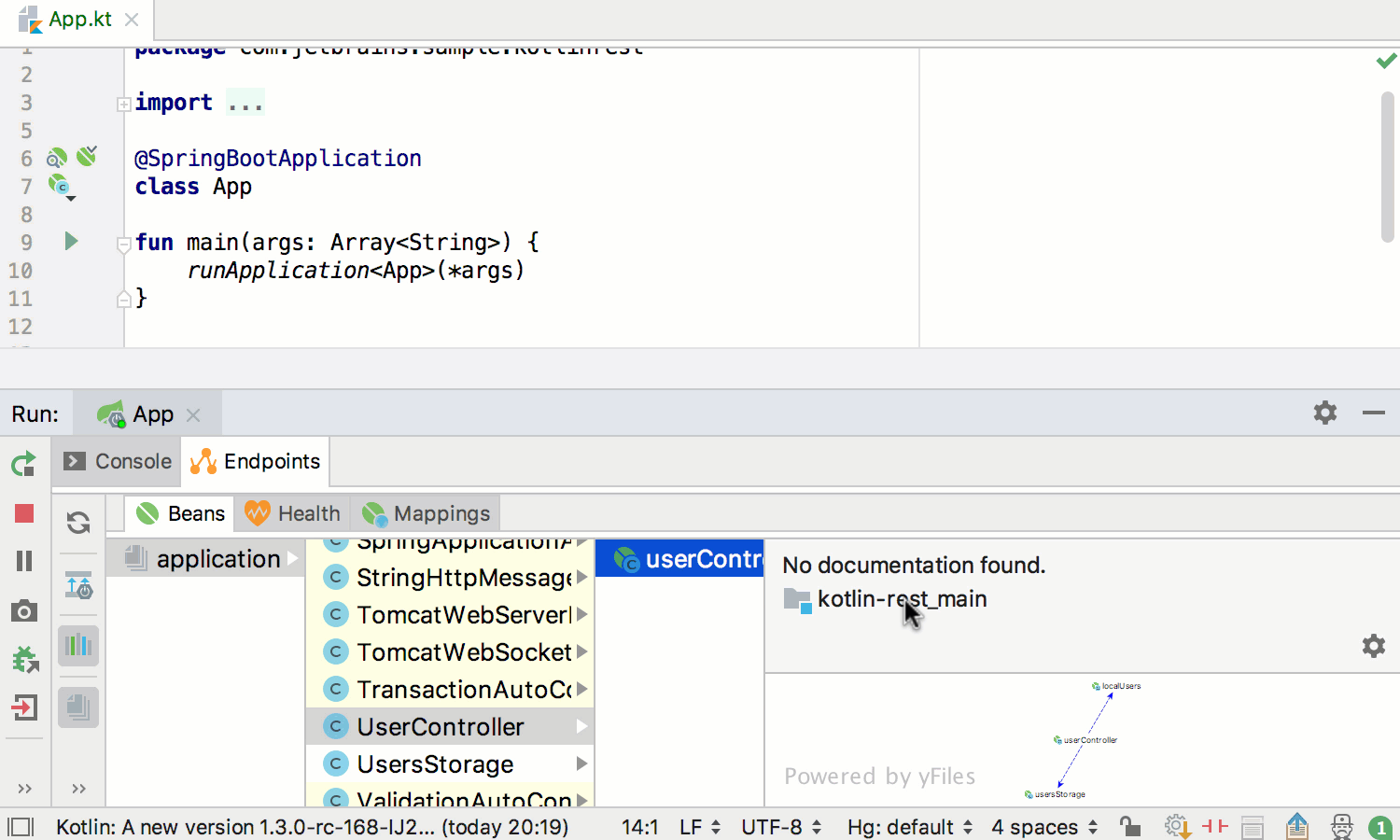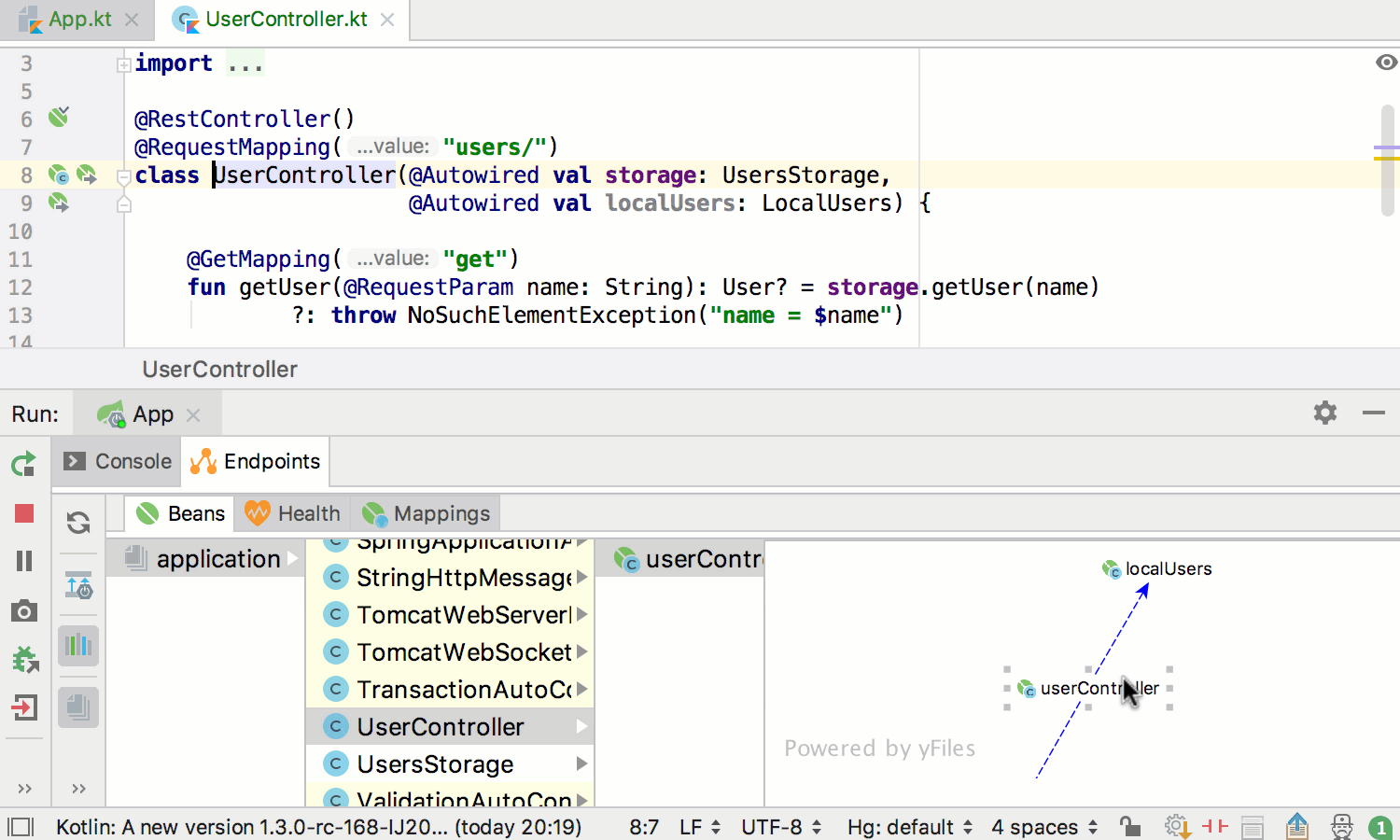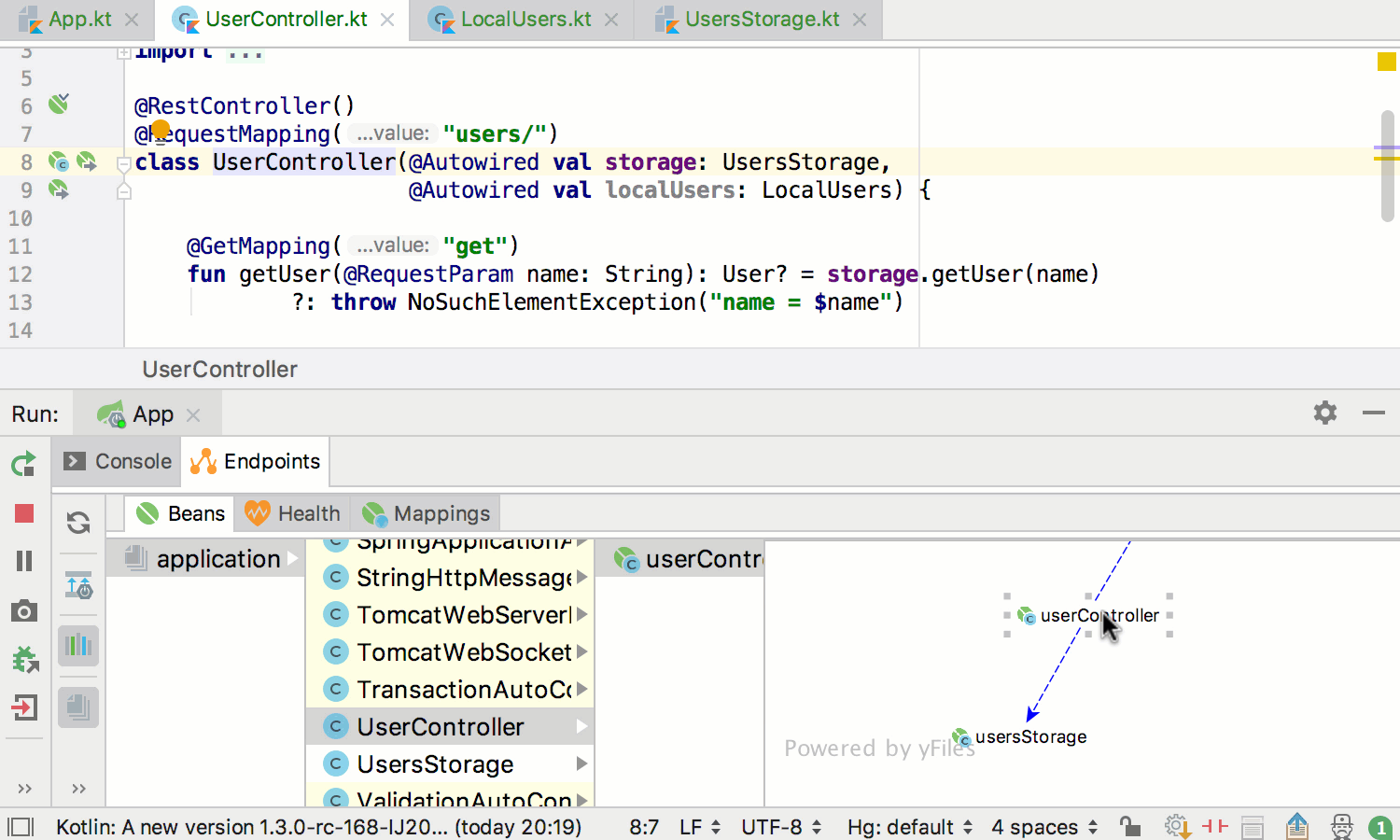
In this latest post about Kotlin support in Spring plugins in IntelliJ IDEA, we’d like to point out that Spring Boot is also fully supported for Kotlin. When you run a Kotlin main function that starts a Spring Boot application, it will be automatically recognized as a Spring Boot Run configuration:
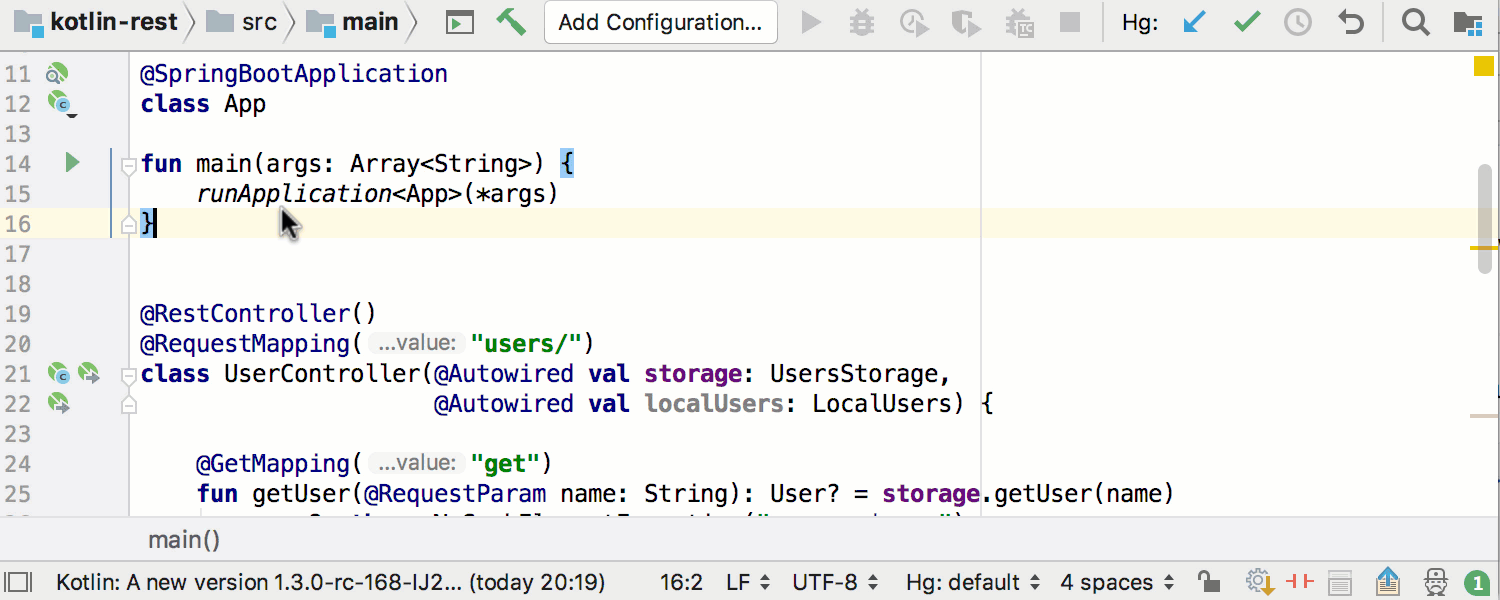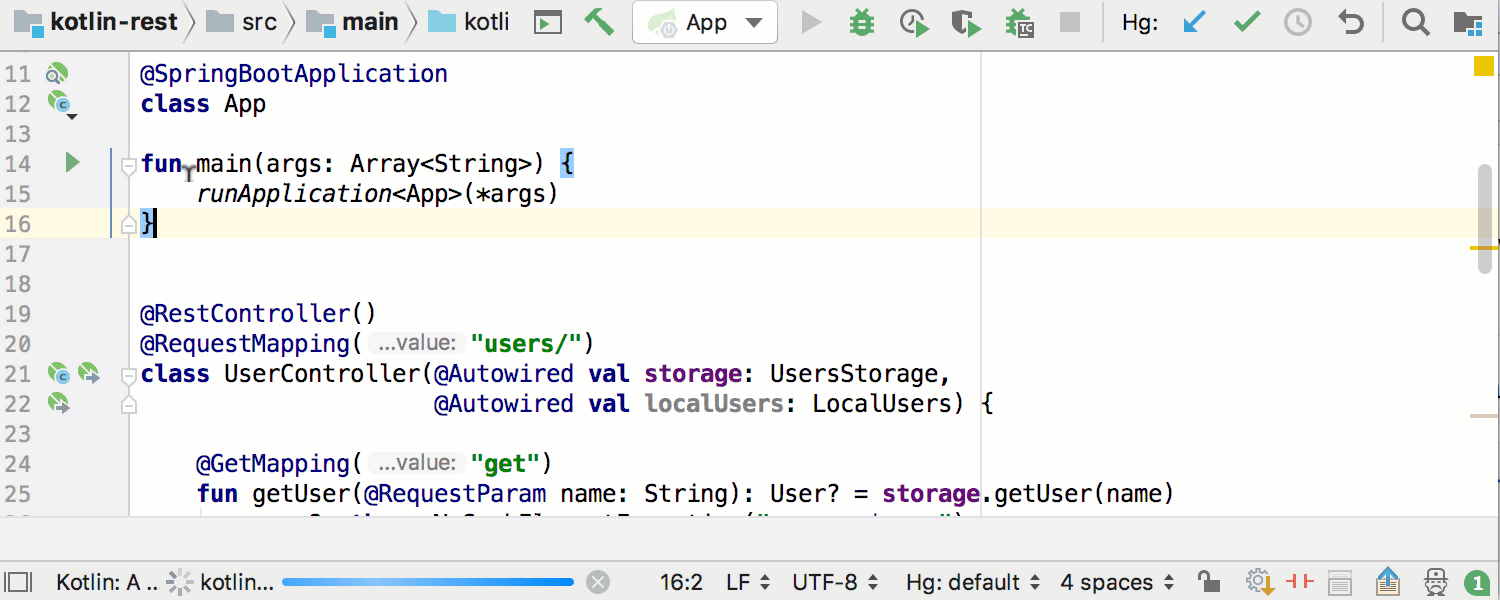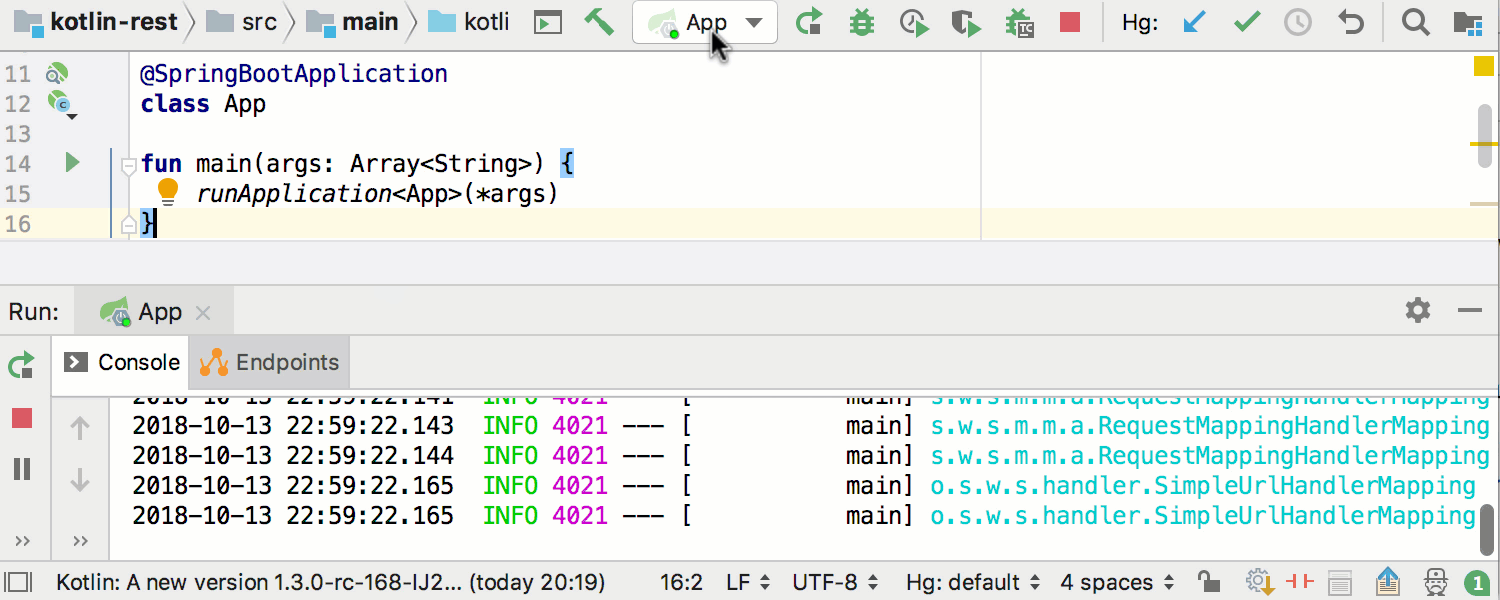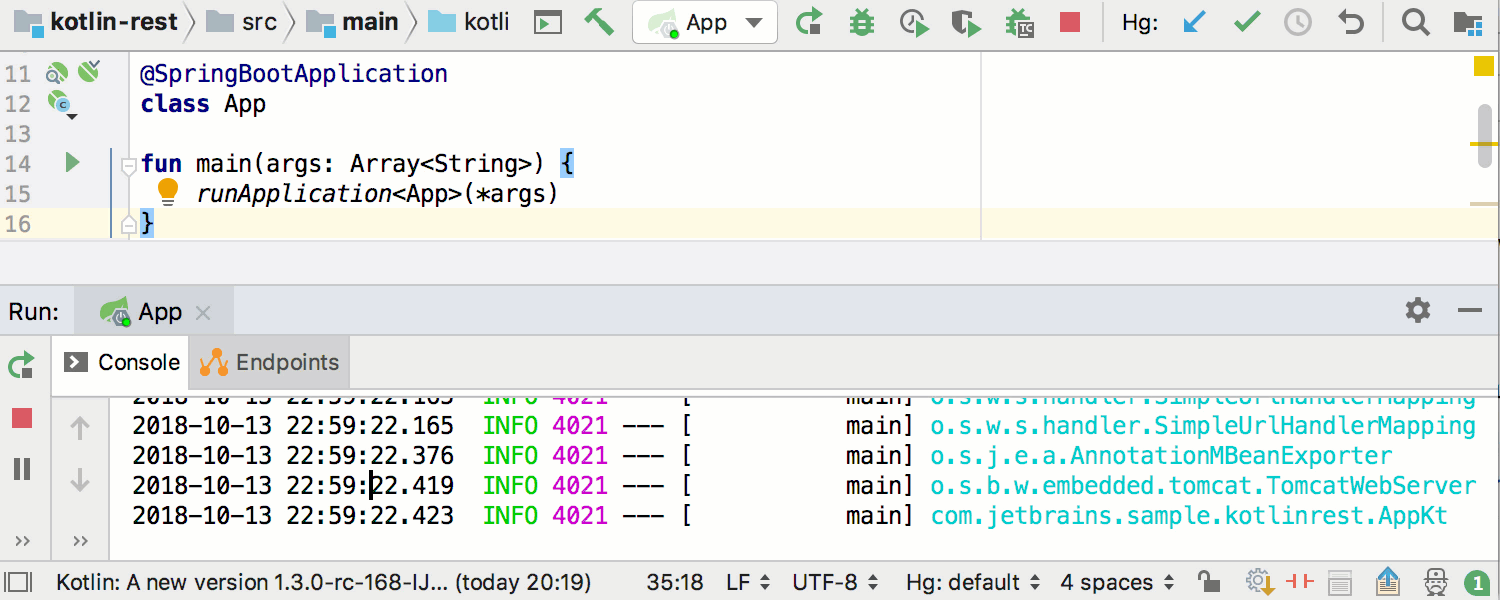
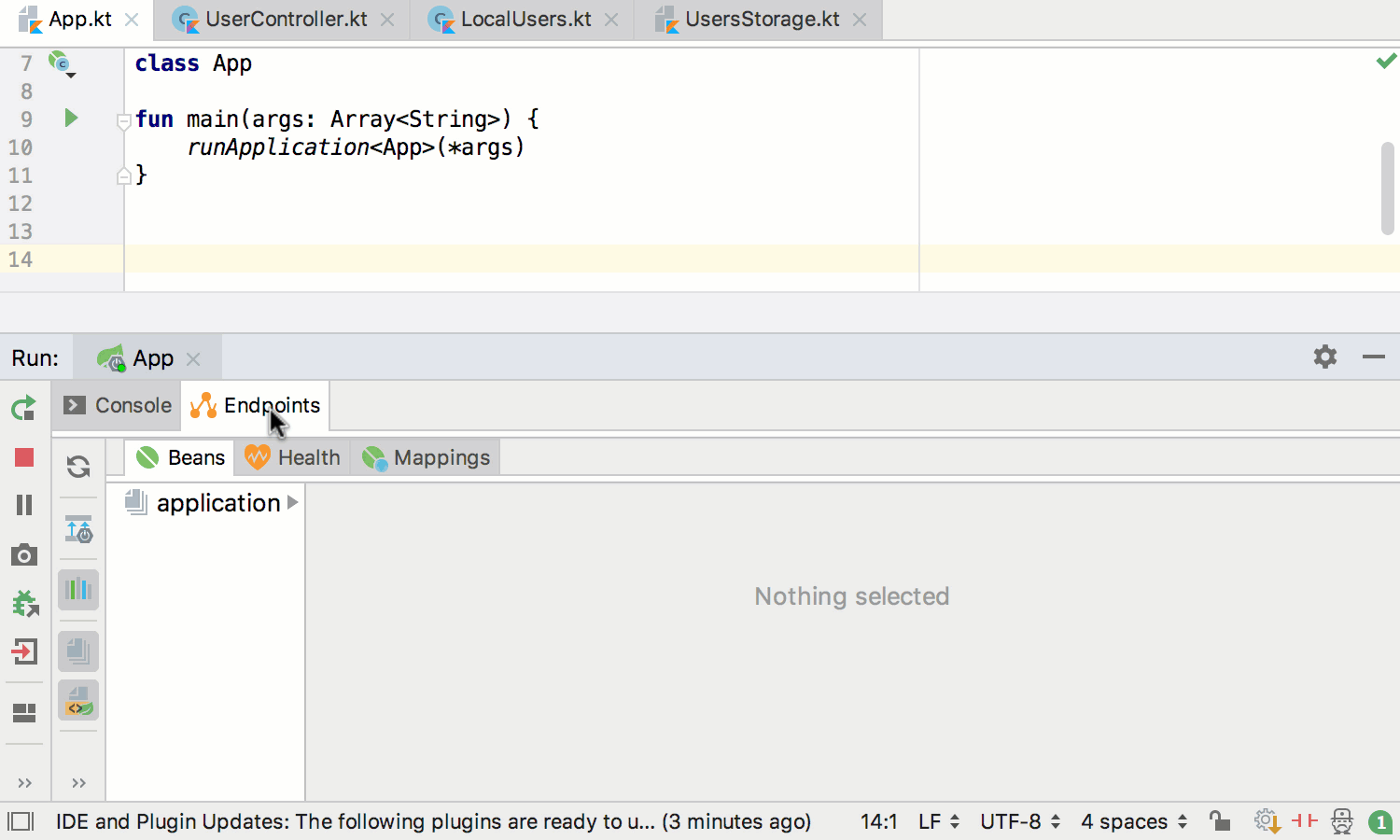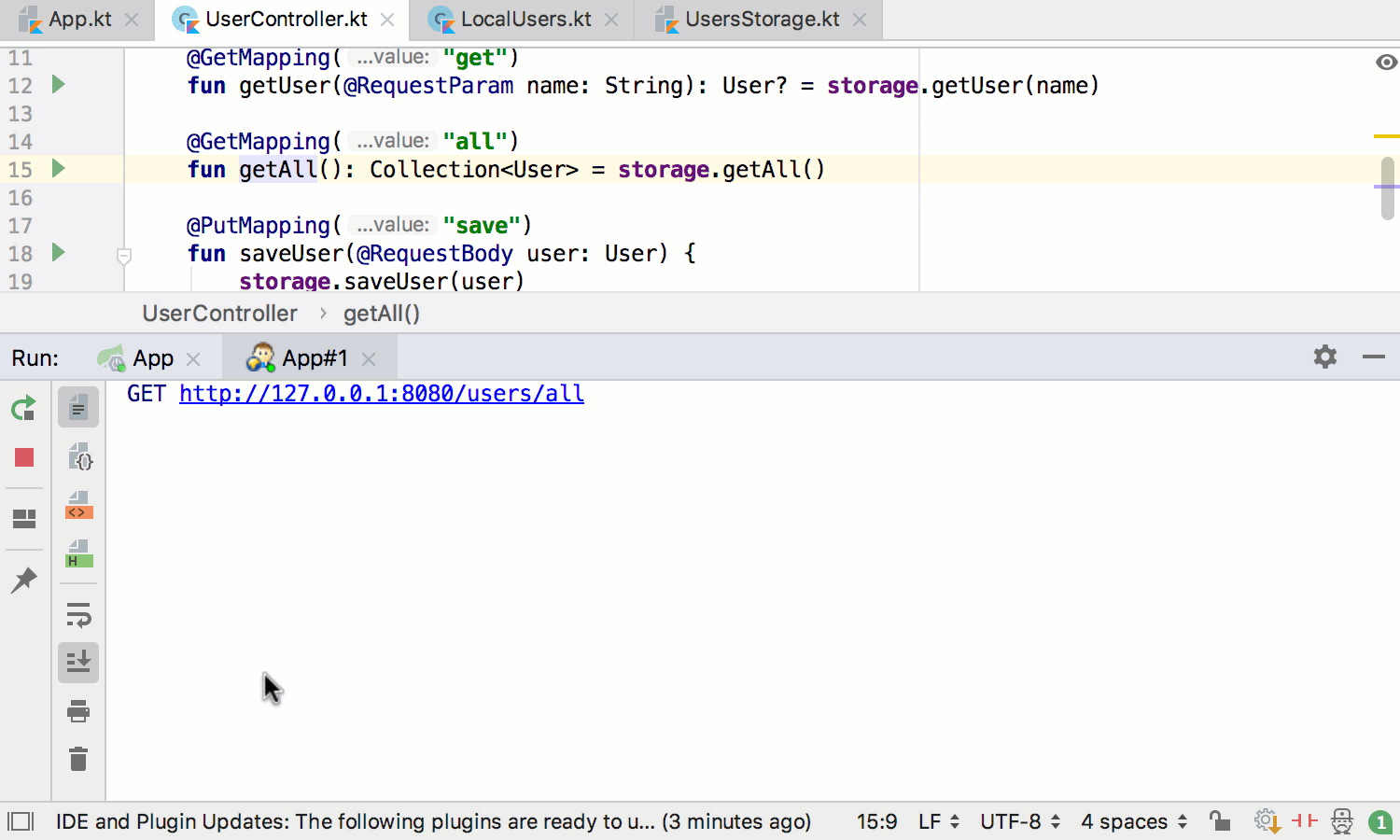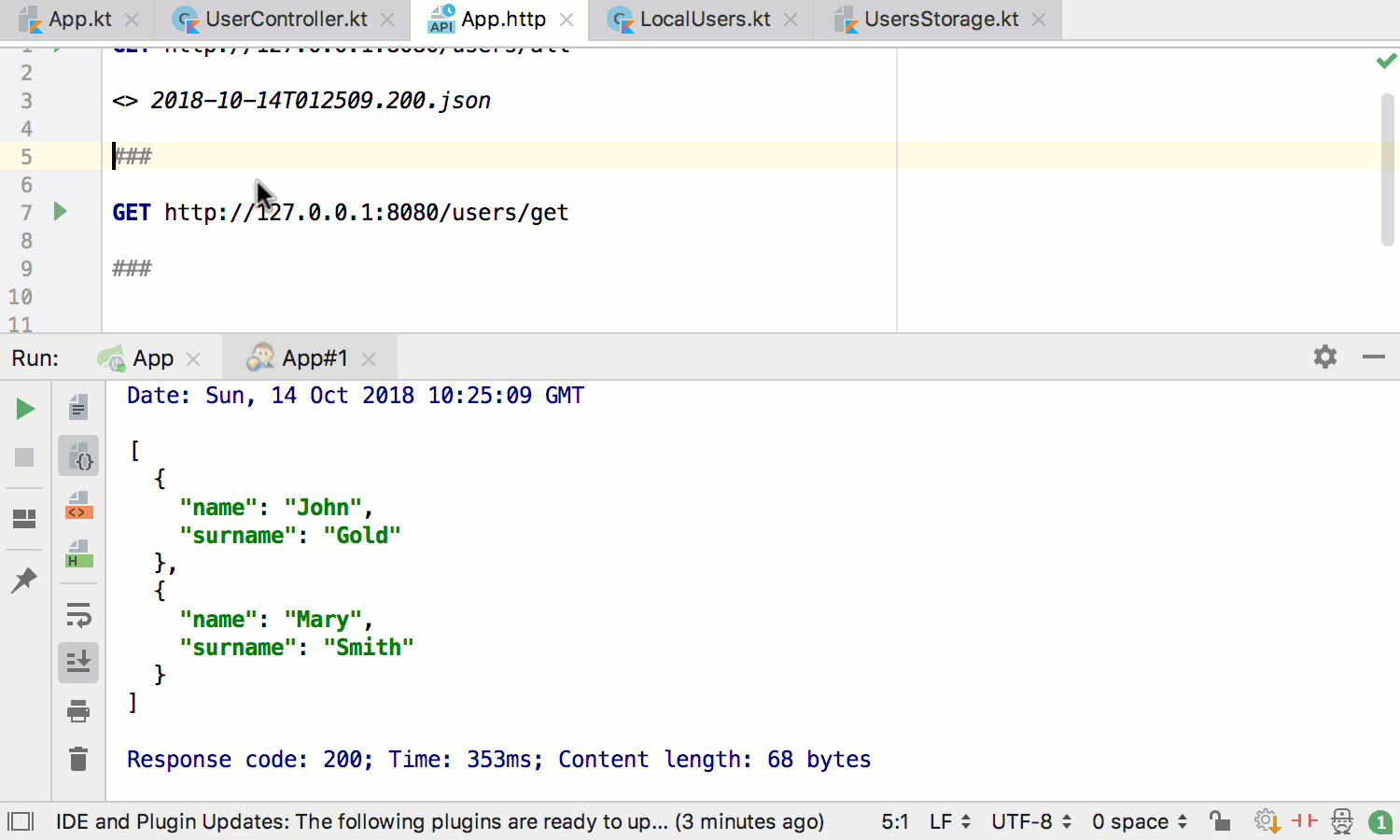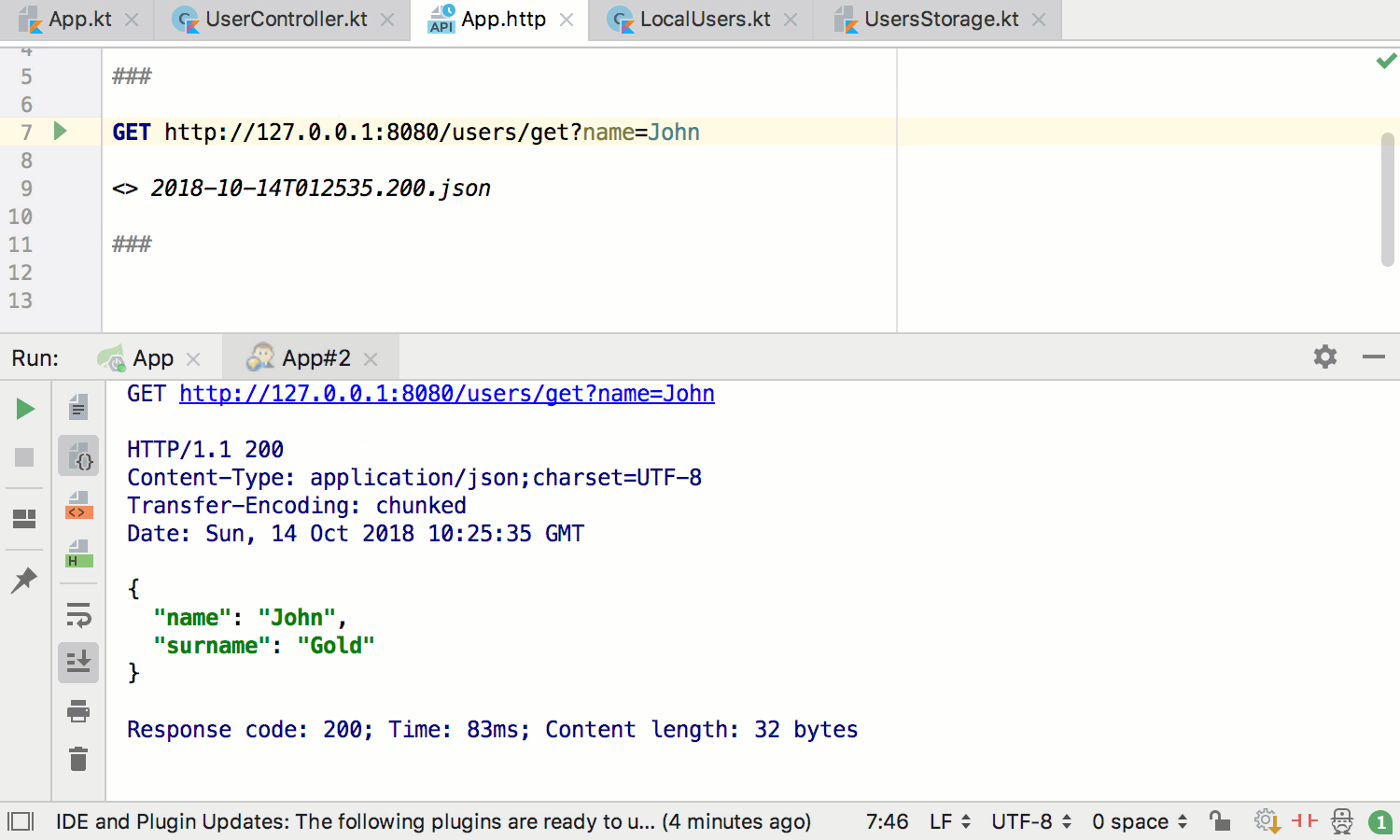
Runtime beans information becomes available via Endpoints:
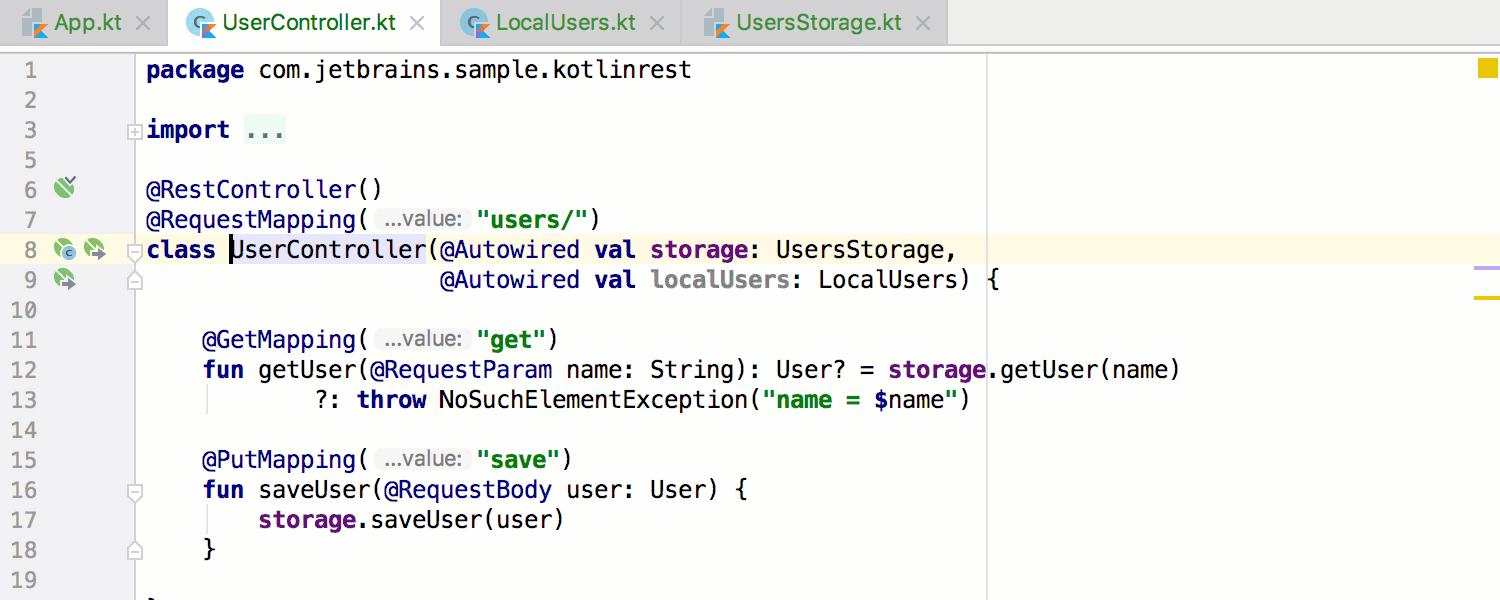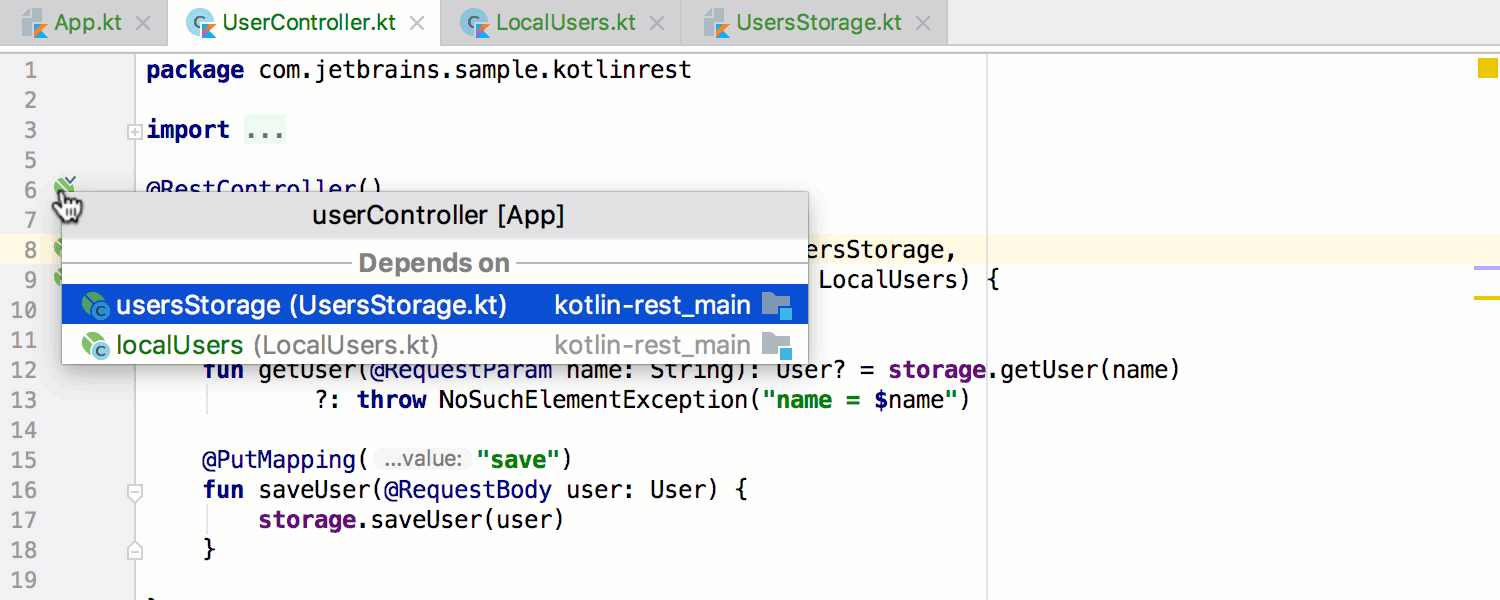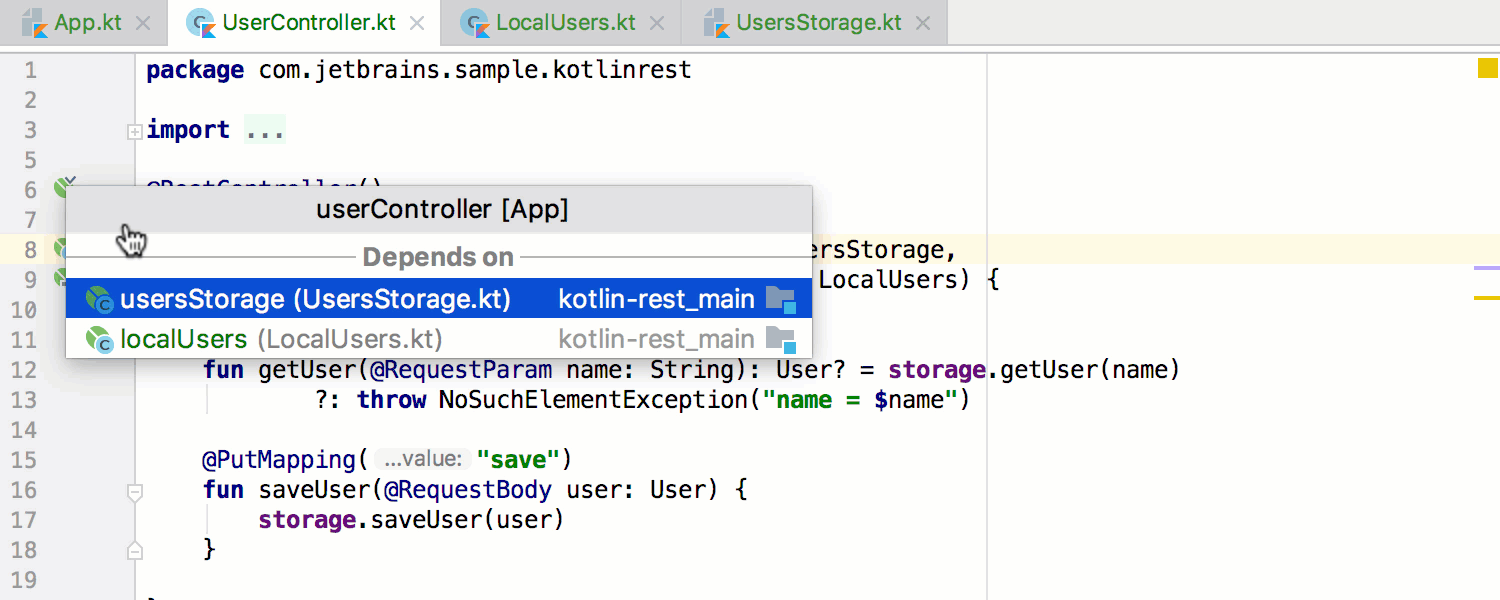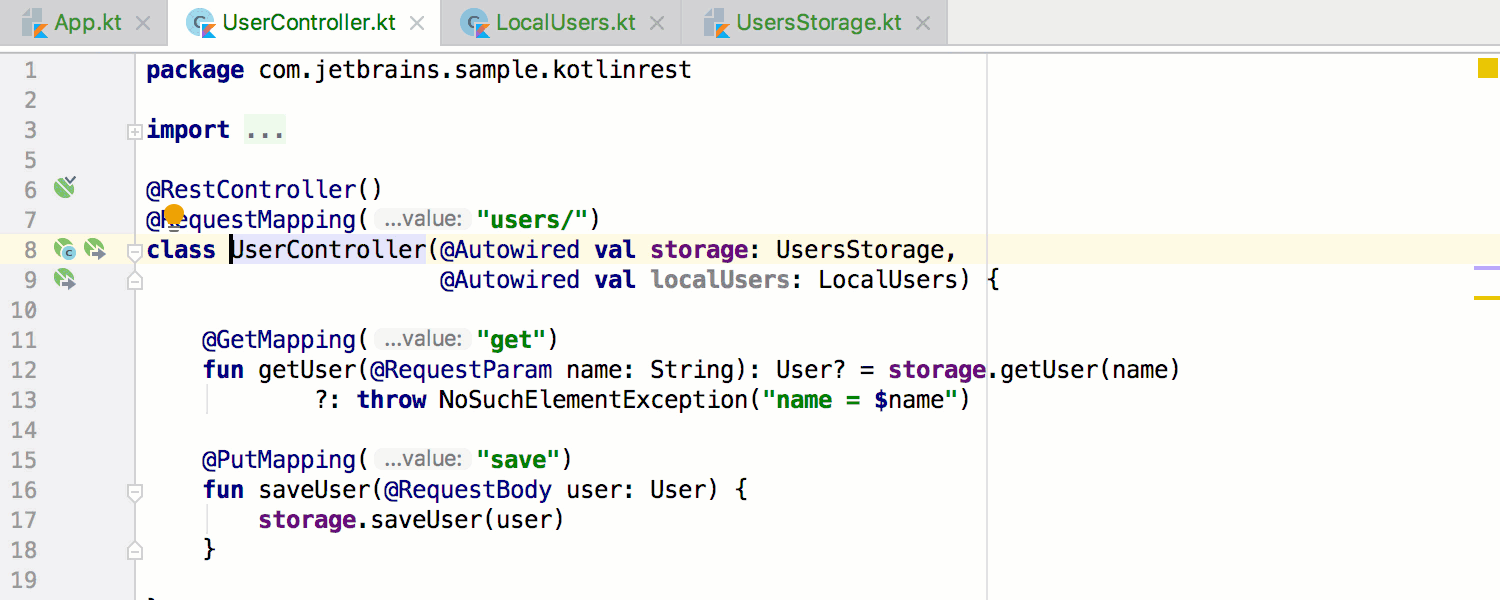
In addition to static-analysis-based gutters, there are runtime dependencies gutter hints appearing near bean declarations:
If you add Spring Boot Actuator to your project, you’ll get additional support for navigating to and testing Spring MVC handlers:
If you use Kotlin to develop Spring Boot apps, especially web services, these features should be a lot of help. Check out other features for Spring in IntelliJ IDEA!
More posts about Kotlin with Spring support in IntelliJ IDEA are coming, so stay tuned!
Subscribe to IntelliJ IDEA Blog updates