ReSharper C++
The Visual Studio Extension for C++ Development
ReSharper C++ 2020.1: New C++20 Features, Improved Coding Assistance, HLSL Support, and More
We are happy to introduce our first major release of the year! Since the start of the EAP, we’ve published a series of blog posts to share news about improvements and new features, step by step. Now it’s time to recap and see what we’ve put together for you in this release!

ReSharper C++ 2020.1 tracks the latest C++20 updates, improves coding assistance and navigation, and helps you be more productive with Unreal Engine 4 and HLSL. Read on for more details about these and other changes in v2020.1:
- C++20 support
- Unreal Engine 4
- HLSL support
- Code analysis and quick-fixes
- Coding assistance
- Code style and formatting
- Enum refactorings
- Navigation improvements
- Unit testing
Update to this version or start a free 30-day trial – the brand new build is available on our site and in the Toolbox App.
C++20 support
At the February meeting in Prague, the ISO C++ committee finished its technical work on C++20, completing the C++20 Committee Draft. ReSharper C++ 2020.1 introduces support for several new features from the latest language standard.
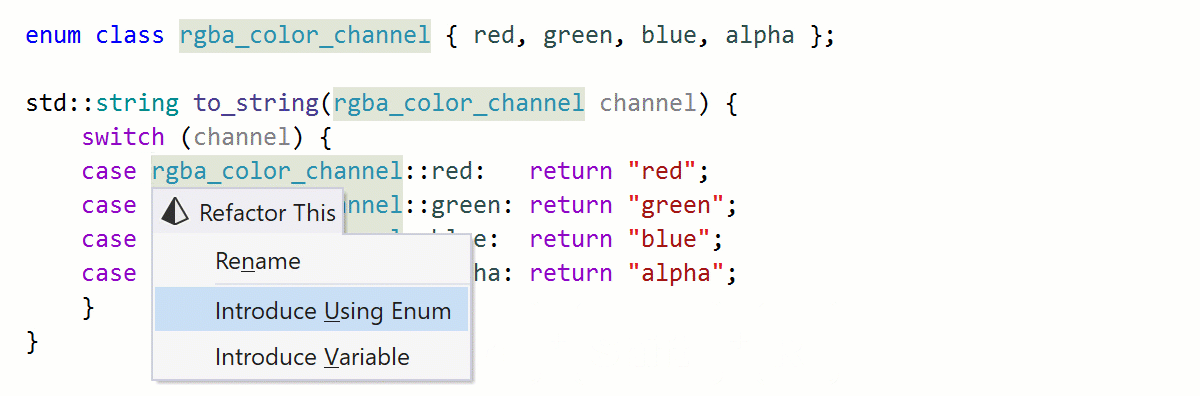
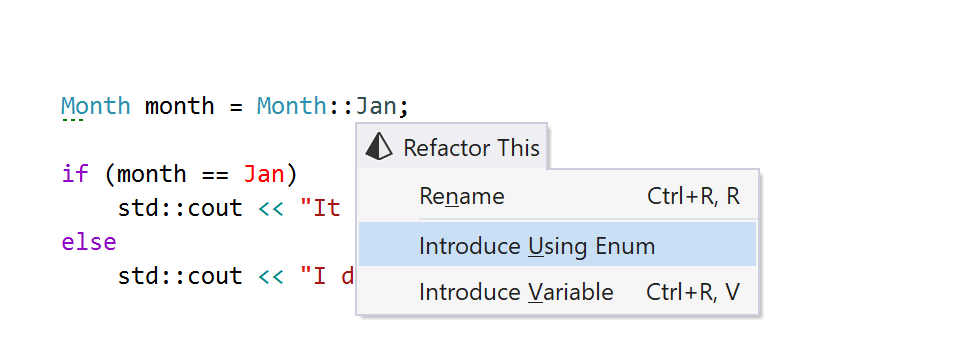
C++20 improves using declarations to support bringing specific enumerators into the local scope (see P1099). The new using enum syntax allows you to add all the enumerators from the target enumeration and omit the name repetitions. ReSharper C++ 2020.1 adds support for using enum declarations, and a new refactoring, Introduce Using Enum, helps you add using enum declarations to existing code.
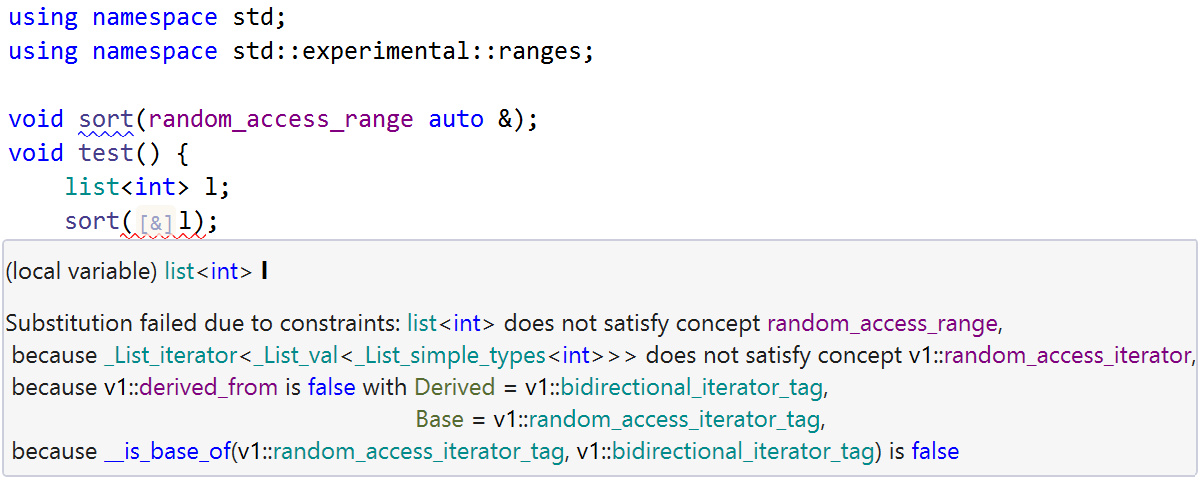
For C++20’s Concepts, we’ve added support for the new syntax for constrained type placeholders and abbreviated function templates (see P1141). Now you can constrain an auto type with a concept and declare a template function with an auto or concept auto placeholder in the list of parameters. Also, we’ve improved error messages about unsatisfied constraints to help you easily understand what went wrong during template substitution.
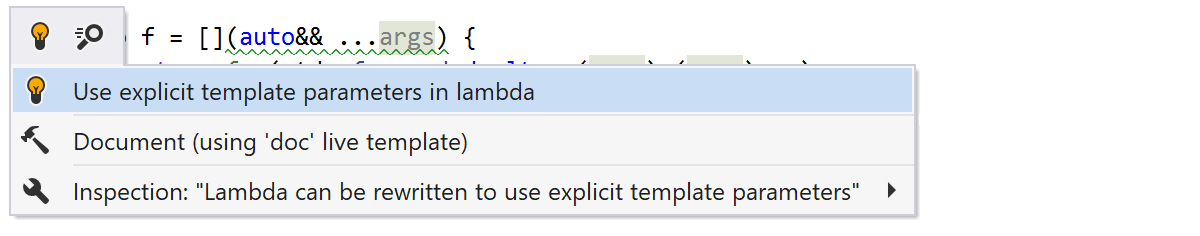
Finally, ReSharper C++ suggests a new quick-fix to use the C++20 template syntax for lambdas (see P0428) when doing so helps simplify your code. For example, you can now use the familiar perfect forwarding syntax for lambdas without having to use decltype on the lambda parameter:
We’re planning to continue our work on C++20 support. Right now, we are enhancing the evaluation of constexpr functions and extending support for the “spaceship” three-way comparison operator. So stay tuned!
Unreal Engine 4
ReSharper C++ 2020.1 improves conformance to the Unreal Engine coding standard. We’ve updated the naming rules to handle console variables and log categories, and the “Use auto” inspection is now hidden by default in UE4 projects.
When renaming a class or a file, the Rename refactoring now updates the corresponding *.generated.h include directives and related files with the A, F, E, T, S, and U prefixes.
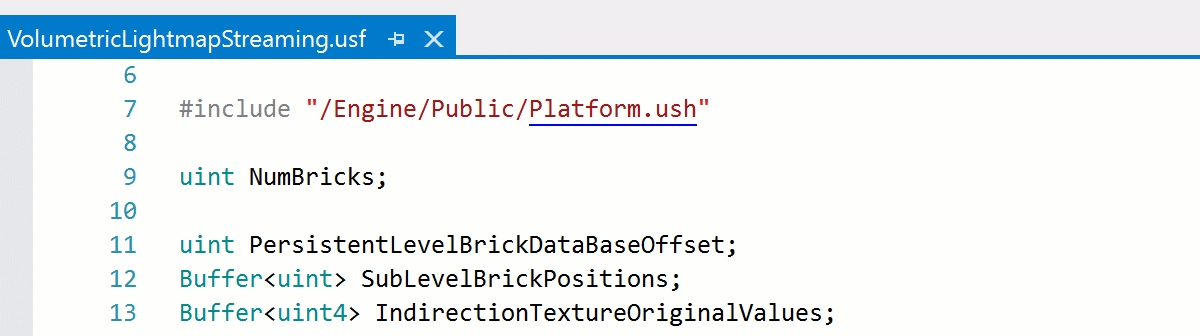
The Unreal Engine USF files are now supported along with their virtual file paths:
A small but pleasant navigation improvement: you can now navigate to namespaces that contain an enumeration in the Unreal Engine style from Search Everywhere/Go to.
ReSharper C++ 2020.1 introduces support for SpatialOS GDK, an Unreal Engine 4 fork that helps you run and manage online games in the cloud:
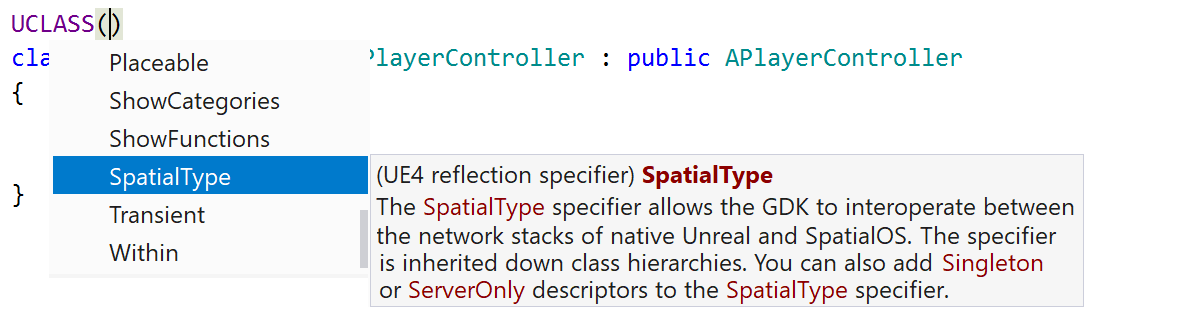
Finally, we’ve made sure ReSharper C++ 2020.1 is compatible with the upcoming Unreal Engine 4.25 release. Note that if you want to work on an UE 4.25 project with a previous version of ReSharper C++, make sure you disable the “Read project properties asynchronously” setting in ReSharper | Options | Code Editing | C++ | Performance.
HLSL support
ReSharper C++ 2020.1 introduces initial support for one more aspect of game development – the High Level Shading Language. Watch a short demo of our HLSL support:
ReSharper C++ highlights HLSL code according to your default color scheme and displays inlay hints and tooltips for code elements with type information and documentation:

You can also search for and quickly navigate to structs, functions, or parameters in your entire solution, referenced files, and standard libraries.
And to perfect the HLSL experience, ReSharper C++ provides smart suggestions in completion lists, highlights the signature compatible with the entered parameters, auto-inserts matching delimiters, and more.
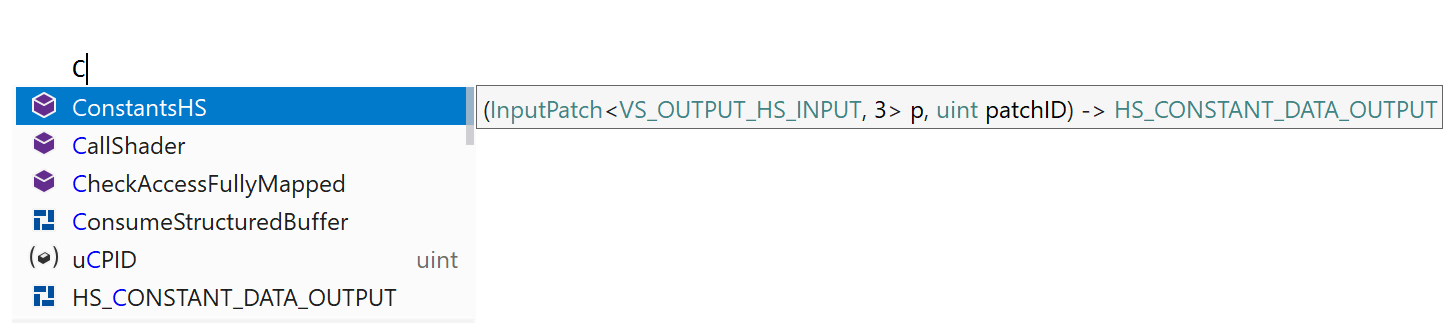
The HLSL support is still in its early stages, so there are a few limitations here. In the next release, we are planning to address code completion for built-in intrinsic functions and also to improve search and navigation for the constant and texture buffers.
Code analysis and quick-fixes
New inspections detect more cases when you should prefer static_cast and offer the corresponding quick-fixes to help you update your code:
reinterpret_castused instead of astatic_castwhen casting tovoid*.- Functional-style cast used instead of a C++ cast.

Moreover, there are two new inspections with quick-fixes for lambda expressions:
- Unused lambda capture – if a local variable is captured by a lambda but is not used inside the lambda body, ReSharper C++ notifies you and suggests removing the unused capture.
- Lambda can be rewritten to use explicit template parameters – ReSharper C++ suggests you use the new С++20 template syntax for lambdas for better code readability.

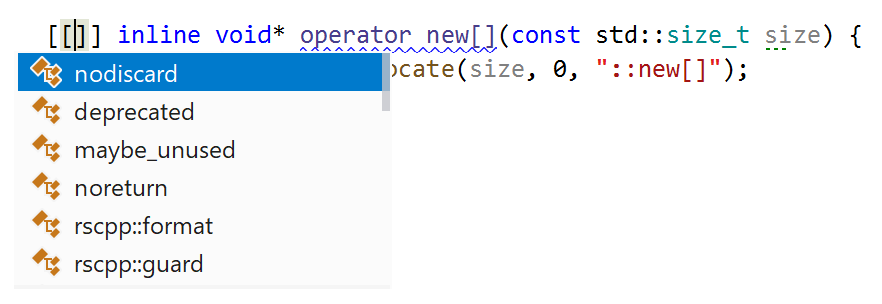
And two more features help you adopt the C++17 maybe_unused attribute:
- A context action to replace
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETERandQ_UNUSEDannotations with[[maybe_unused]]. - A quick-fix to add
[[maybe_unused]]to an unused parameter or variable.
![[[maybe_unused]]](https://blog.jetbrains.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/rscpp-maybe_unused_attr.png)
We’ve also upgraded the bundled Clang-Tidy binary to Clang 10, bringing along more than 70 new checks and compiler diagnostics.
Coding assistance
Two well-known features from ReSharper for .NET have finally come to ReSharper C++ – Rearrange Code and Complete Statement.
Rearrange Code quickly moves code elements around, expands or shrinks the current scope, and more. To rearrange code, press Ctrl+Shift+Alt over the code element or selection that you want to move, then press any arrow key:
- The Move up and Move down commands rearrange elements within a specific scope up and down relative to other elements in this scope, or between neighboring scopes.

- Move left and Move right can rearrange elements that are normally written in a single line and can move a statement or a declaration into the region that directly follows it or outside the current region.

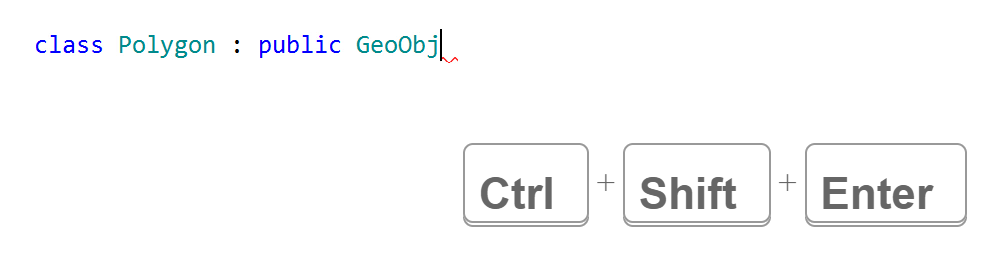
Complete Statement inserts the required syntax elements to finish the current statement and puts the caret in the right place. Use the Ctrl+Shift+Enter shortcut instead of having to perform lots of other small actions:
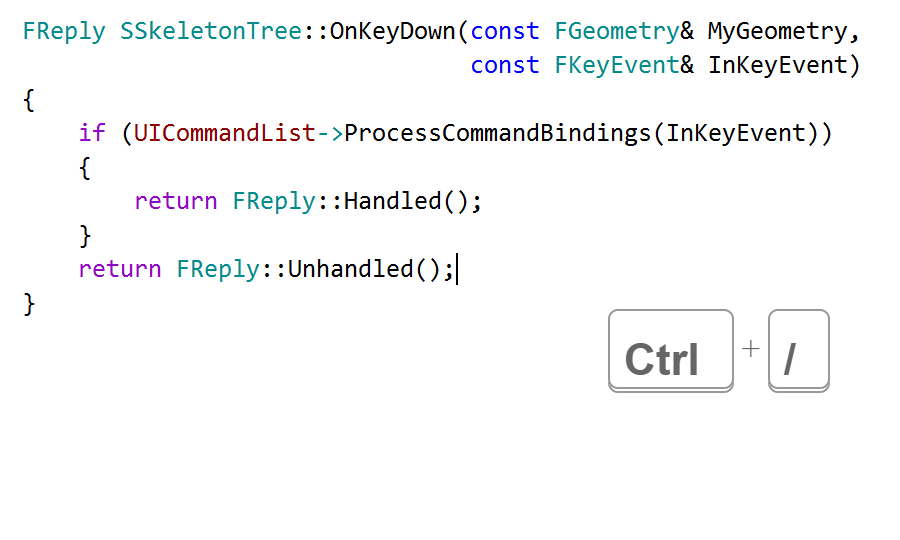
The new Document editor action, bound to Ctrl+/ in the Visual Studio keymap, lets you quickly generate a documentation comment for the nearby code element instead of using the context action:
The completion list now suggests standard C++ attributes, label names for the goto statement, the new std::forward postfix template, and arguments for calls to a base function. In addition, code completion now works in macro definitions.
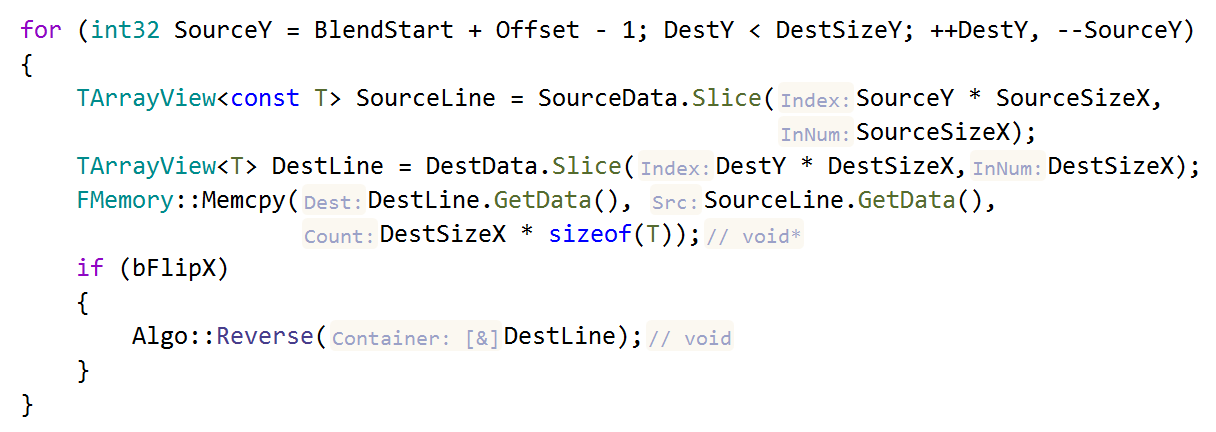
Parameter and type name hints became an inherent aspect of the development experience with ReSharper C++ (check out our post about all the available hints). And now they are available in dependent code as well:
Also, with improved typing assistance, you can now select any piece of code and type a parenthesis, brace, bracket, or quote to surround the selection with the corresponding characters.
Code style and formatting
Along with many fixes, the formatting engine in ReSharper C++ 2020.1 gains full support for the syntax of C++20 concepts. We’ve also added several new formatting options, including an option for the double indentation of class members and an option to control spaces before parentheses in lambda parameters.
In ReSharper C++ 2019.3 we introduced support for sorting of #include directives. In this release, we’ve added an ability to import the sorting settings from a .clang-format file. Make sure that Read code style form .clang-format style is checked on the ReSharper | Options | Code Editing | General Formatter Style settings page, and ReSharper C++ will use the IncludeBlocks, IncludeCategories, IncludeIsMainRegex, and SortIncludes settings from your .clang-format file to sort the #include directives in the same way that clang-format does.
Moreover, ReSharper C++ 2020.1 provides two additional settings for the better configurability of #includes sorting behavior:
- Case-sensitive sort – used to place all include directives starting with uppercase letters before those starting with lowercase letters.
- Group headers by directory – used to create groups of headers based on their file path.

Enum refactorings
We’ve added two new refactorings to help you modernize your enum usage according to the language changes in the C++11 and C++20 standards.
The Convert to Scoped Enum refactoring converts a C-style enumeration declaration into a C++11 scoped enumeration:
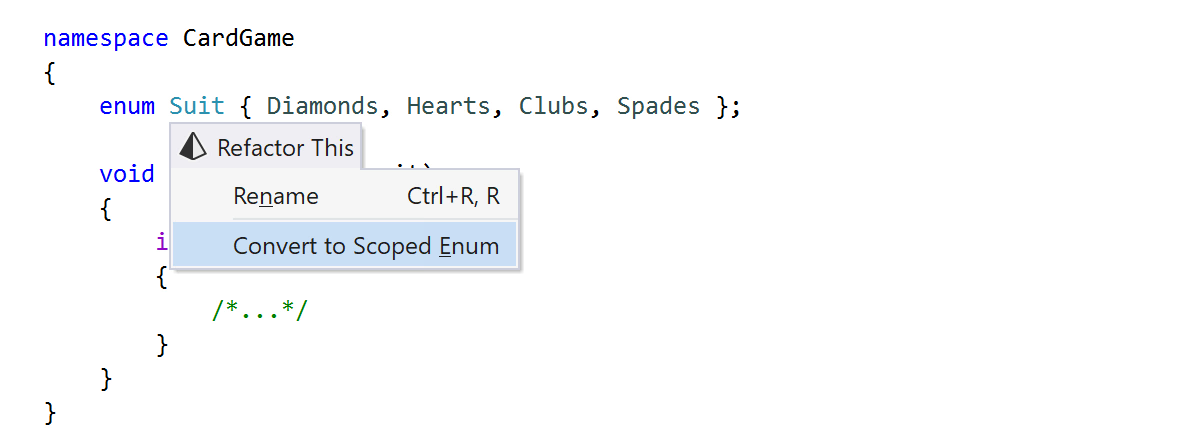
This refactoring will update all the enumeration declarations and qualify the enumerator references. Moreover, if a value of the enumeration type is implicitly cast to an integral type, ReSharper C++ will warn you about this and automatically insert a static_cast to the corresponding type.
The Introduce Using Enum refactoring adds a C++20 using enum declaration to the current scope and shortens the enumerator references:
Navigation improvements
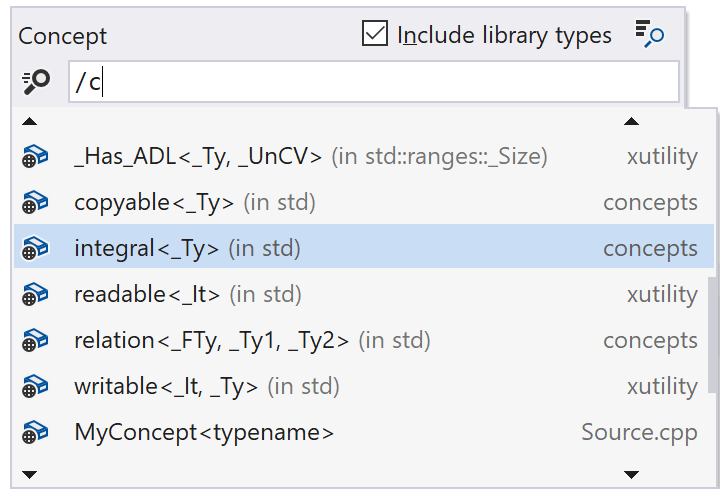
In ReSharper C++ 2020.1, you can navigate to the declaration of any symbol from a matching word inside a comment. Just click the name while holding down the Ctrl key, or click it with the mouse scroll button. By the way, the scroll button navigation is also new.
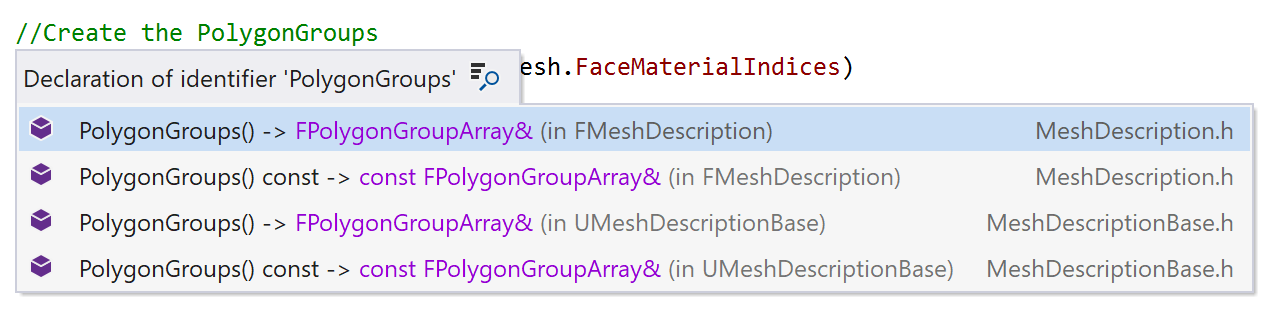
Search Everywhere/Go to includes two new filter categories: concepts and namespaces. Type “/” in the search box to see all the available filters.
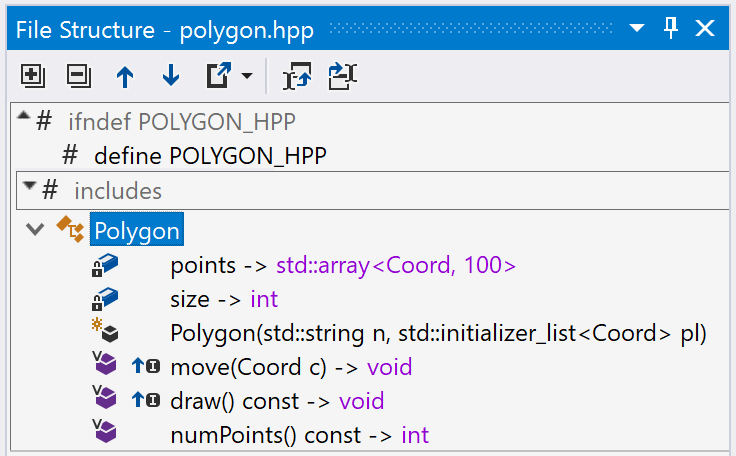
The File Structure window now provides more details for quick file navigation with the following icon indicators:
- Class member accessibility.
- Virtual, static, and pure specifiers.
- Inheritance information for class members when a function overrides, implements, or hides a base function.
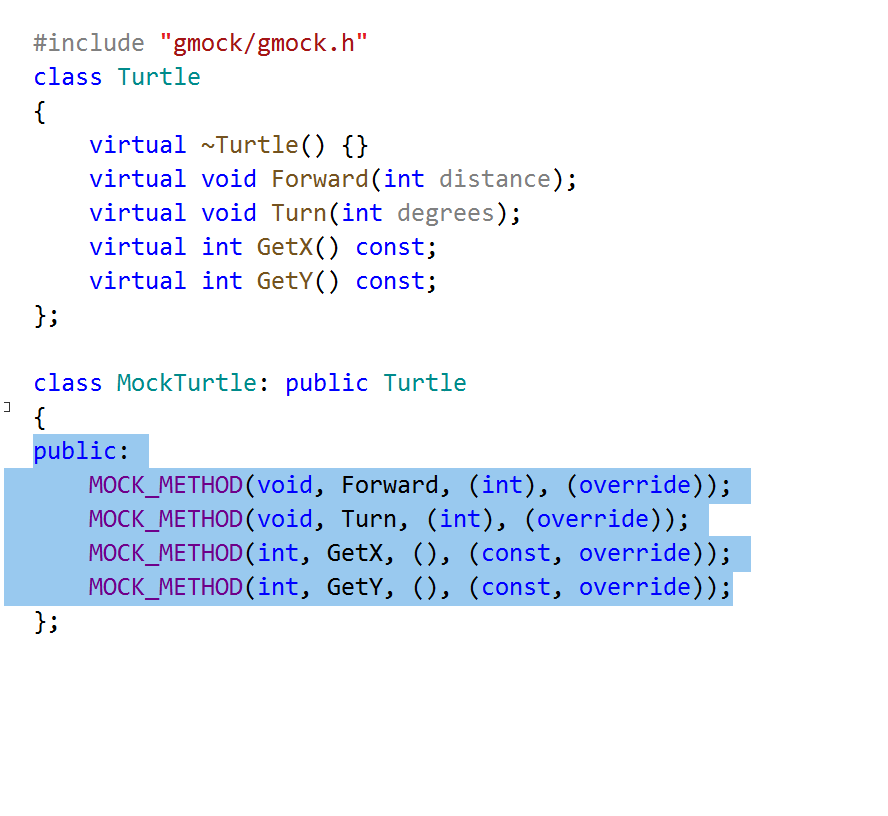
Unit testing
The mock methods generator now supports the MOCK_METHOD macro introduced in GTest 1.10. The family of MOCK_(const_)METHODn() macros used in previous GTest releases is now deprecated.
The test runner in ReSharper C++ uses named pipes to communicate with child test processes to read the unbuffered output. However, in some environments, named pipes might misbehave because of security software. We’ve introduced the new setting Use named pipes to communicate with child processes so you can now disable this option to use temporary files instead.
The full list of new features and bug fixes in this release includes more than 230 issues and is available in our issue tracker. Feel free to submit a new feature request, or upvote any existing one. Your feedback is always welcome!
Also, more changes are coming from the ReSharper platform, so visit its What’s New page, as well.
Get ReSharper C++ 2020.1 and let us know what you think!
Your ReSharper C++ team
JetBrains
The Drive to Develop
Subscribe to ReSharper C++ Blog updates








